Chapter 6 Changes in cluster abundance
6.1 Overview
In a DA analysis, we test for significant changes in per-label cell abundance across conditions. This will reveal which cell types are depleted or enriched upon treatment, which is arguably just as interesting as changes in expression within each cell type. The DA analysis has a long history in flow cytometry (Finak et al. 2014; Lun, Richard, and Marioni 2017) where it is routinely used to examine the effects of different conditions on the composition of complex cell populations. By performing it here, we effectively treat scRNA-seq as a “super-FACS” technology for defining relevant subpopulations using the entire transcriptome. We prepare for the DA analysis by quantifying the number of cells assigned to each label (or cluster) in our WT chimeric experiment (Pijuan-Sala et al. 2019). In this case, we are aiming to identify labels that change in abundance among the compartment of injected cells compared to the background.
#--- loading ---#
library(MouseGastrulationData)
sce.chimera <- WTChimeraData(samples=5:10)
sce.chimera
#--- feature-annotation ---#
library(scater)
rownames(sce.chimera) <- uniquifyFeatureNames(
rowData(sce.chimera)$ENSEMBL, rowData(sce.chimera)$SYMBOL)
#--- quality-control ---#
drop <- sce.chimera$celltype.mapped %in% c("stripped", "Doublet")
sce.chimera <- sce.chimera[,!drop]
#--- normalization ---#
sce.chimera <- logNormCounts(sce.chimera)
#--- variance-modelling ---#
library(scran)
dec.chimera <- modelGeneVar(sce.chimera, block=sce.chimera$sample)
chosen.hvgs <- dec.chimera$bio > 0
#--- merging ---#
library(batchelor)
set.seed(01001001)
merged <- correctExperiments(sce.chimera,
batch=sce.chimera$sample,
subset.row=chosen.hvgs,
PARAM=FastMnnParam(
merge.order=list(
list(1,3,5), # WT (3 replicates)
list(2,4,6) # td-Tomato (3 replicates)
)
)
)
#--- clustering ---#
g <- buildSNNGraph(merged, use.dimred="corrected")
clusters <- igraph::cluster_louvain(g)
colLabels(merged) <- factor(clusters$membership)
#--- dimensionality-reduction ---#
merged <- runTSNE(merged, dimred="corrected", external_neighbors=TRUE)
merged <- runUMAP(merged, dimred="corrected", external_neighbors=TRUE)abundances <- table(merged$celltype.mapped, merged$sample)
abundances <- unclass(abundances)
head(abundances)##
## 5 6 7 8 9 10
## Allantois 97 15 139 127 318 259
## Blood progenitors 1 6 3 16 6 8 17
## Blood progenitors 2 31 8 28 21 43 114
## Cardiomyocytes 85 21 79 31 174 211
## Caudal Mesoderm 10 10 9 3 10 29
## Caudal epiblast 2 2 0 0 22 456.2 Performing the DA analysis
Our DA analysis will again be performed with the edgeR package. This allows us to take advantage of the NB GLM methods to model overdispersed count data in the presence of limited replication - except that the counts are not of reads per gene, but of cells per label (Lun, Richard, and Marioni 2017). The aim is to share information across labels to improve our estimates of the biological variability in cell abundance between replicates.
library(edgeR)
# Attaching some column metadata.
extra.info <- colData(merged)[match(colnames(abundances), merged$sample),]
y.ab <- DGEList(abundances, samples=extra.info)
y.ab## An object of class "DGEList"
## $counts
##
## 5 6 7 8 9 10
## Allantois 97 15 139 127 318 259
## Blood progenitors 1 6 3 16 6 8 17
## Blood progenitors 2 31 8 28 21 43 114
## Cardiomyocytes 85 21 79 31 174 211
## Caudal Mesoderm 10 10 9 3 10 29
## 29 more rows ...
##
## $samples
## group lib.size norm.factors batch cell barcode sample stage
## 5 1 2298 1 5 cell_9769 AAACCTGAGACTGTAA 5 E8.5
## 6 1 1026 1 6 cell_12180 AAACCTGCAGATGGCA 6 E8.5
## 7 1 2740 1 7 cell_13227 AAACCTGAGACAAGCC 7 E8.5
## 8 1 2904 1 8 cell_16234 AAACCTGCAAACCCAT 8 E8.5
## 9 1 4057 1 9 cell_19332 AAACCTGCAACGATCT 9 E8.5
## 10 1 6401 1 10 cell_23875 AAACCTGAGGCATGTG 10 E8.5
## tomato pool stage.mapped celltype.mapped closest.cell
## 5 TRUE 3 E8.25 Mesenchyme cell_24159
## 6 FALSE 3 E8.25 Somitic mesoderm cell_63247
## 7 TRUE 4 E8.5 Somitic mesoderm cell_25454
## 8 FALSE 4 E8.25 ExE mesoderm cell_139075
## 9 TRUE 5 E8.0 ExE mesoderm cell_116116
## 10 FALSE 5 E8.5 Forebrain/Midbrain/Hindbrain cell_39343
## doub.density sizeFactor label
## 5 0.029850 1.6349 19
## 6 0.291916 2.5981 6
## 7 0.601740 1.5939 17
## 8 0.004733 0.8707 9
## 9 0.079415 0.8933 15
## 10 0.040747 0.3947 1We filter out low-abundance labels as previously described. This avoids cluttering the result table with very rare subpopulations that contain only a handful of cells. For a DA analysis of cluster abundances, filtering is generally not required as most clusters will not be of low-abundance (otherwise there would not have been enough evidence to define the cluster in the first place).
## Mode FALSE TRUE
## logical 10 24Unlike DE analyses, we do not perform an additional normalization step with calcNormFactors().
This means that we are only normalizing based on the “library size”, i.e., the total number of cells in each sample.
Any changes we detect between conditions will subsequently represent differences in the proportion of cells in each cluster.
The motivation behind this decision is discussed in more detail in Section 6.3.
We formulate the design matrix with a blocking factor for the batch of origin for each sample and an additive term for the td-Tomato status (i.e., injection effect). Here, the log-fold change in our model refers to the change in cell abundance after injection, rather than the change in gene expression.
We use the estimateDisp() function to estimate the NB dispersion for each cluster (Figure 6.1).
We turn off the trend as we do not have enough points for its stable estimation.
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 0.0614 0.0614 0.0614 0.0614 0.0614 0.0614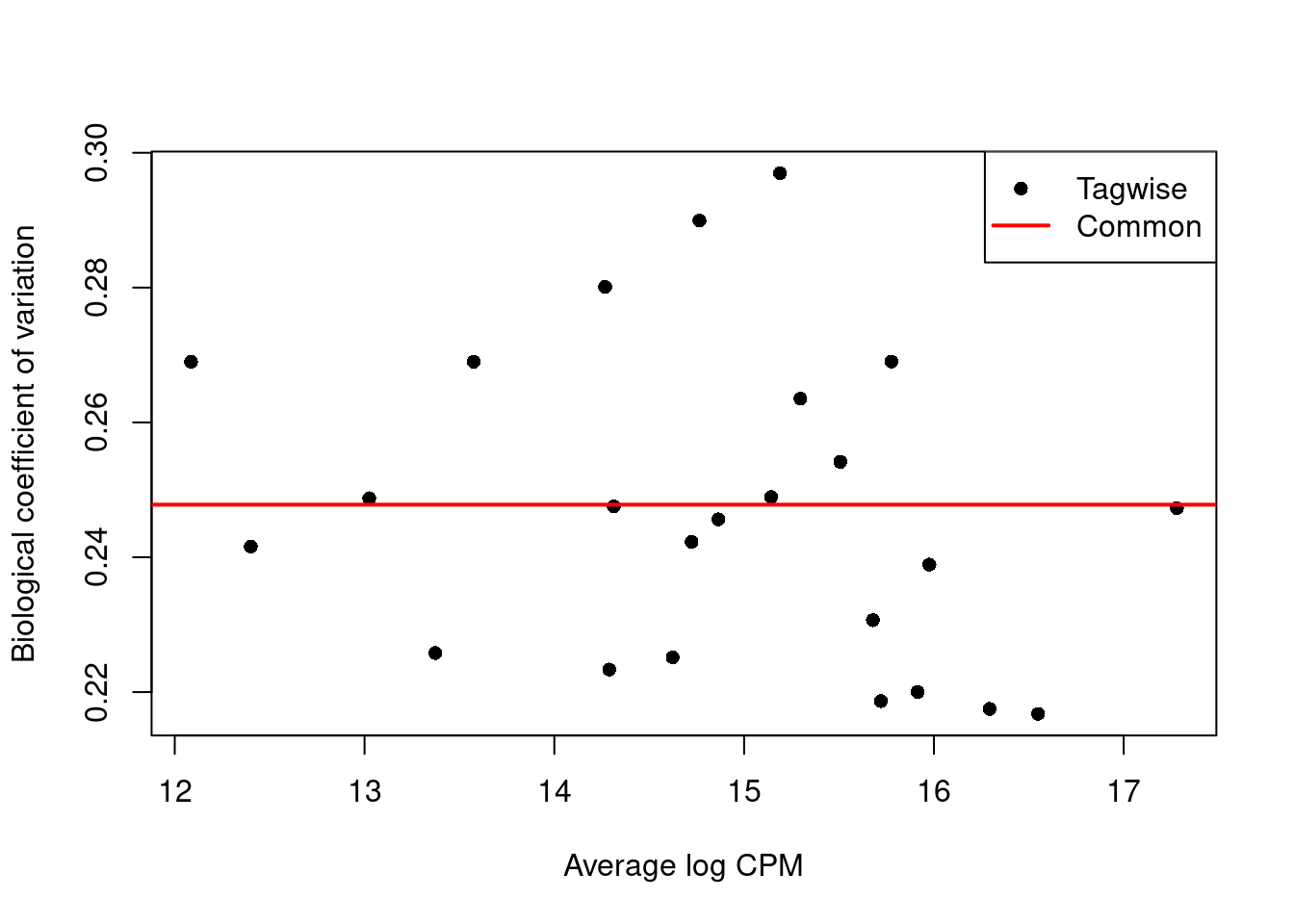
Figure 6.1: Biological coefficient of variation (BCV) for each label with respect to its average abundance. BCVs are defined as the square root of the NB dispersion. Common dispersion estimates are shown in red.
We repeat this process with the QL dispersion, again disabling the trend (Figure 6.2).
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf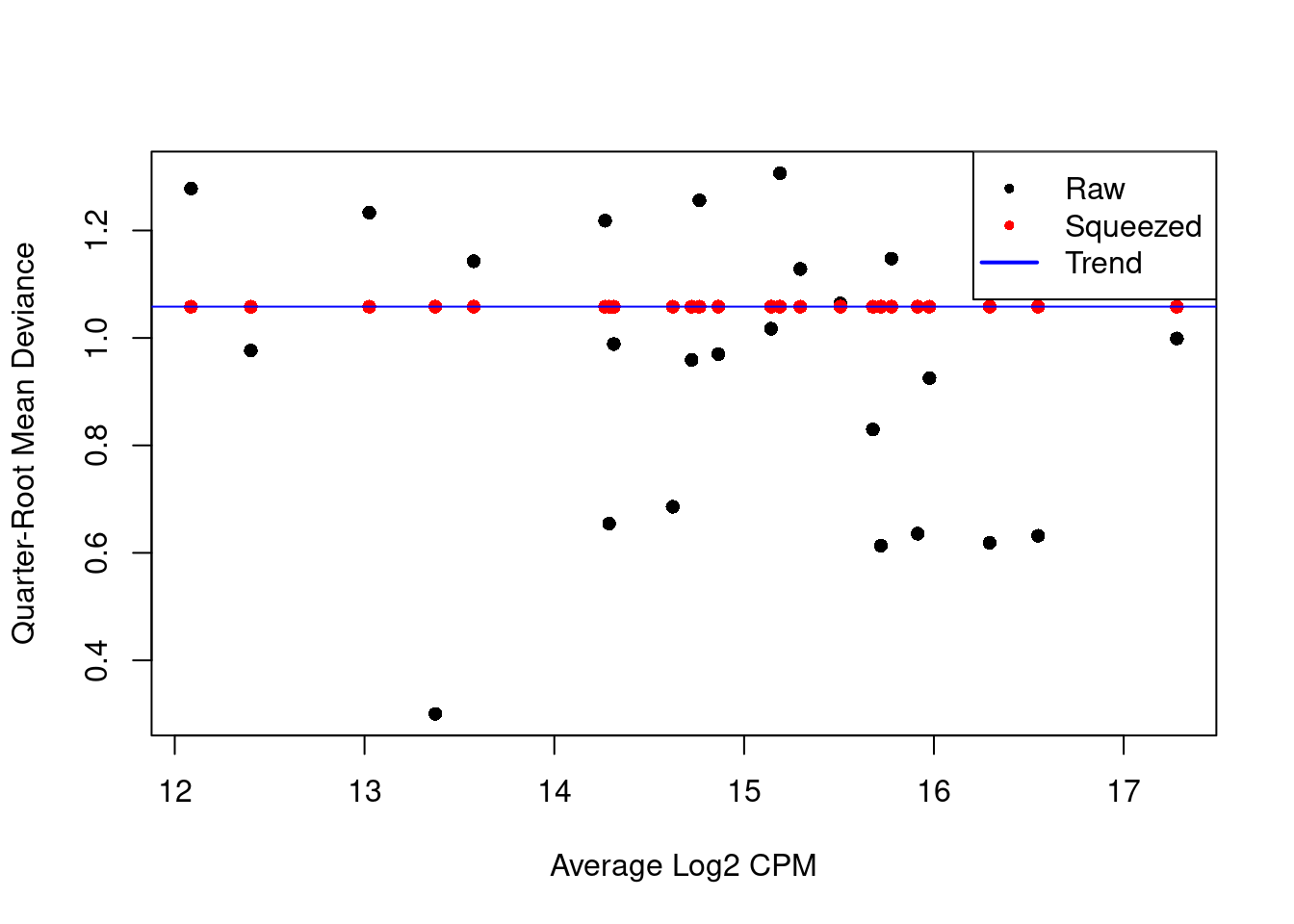
Figure 6.2: QL dispersion estimates for each label with respect to its average abundance. Quarter-root values of the raw estimates are shown in black while the shrunken estimates are shown in red. Shrinkage is performed towards the common dispersion in blue.
We test for differences in abundance between td-Tomato-positive and negative samples using glmQLFTest().
We see that extra-embryonic ectoderm is strongly depleted in the injected cells.
This is consistent with the expectation that cells injected into the blastocyst should not contribute to extra-embryonic tissue.
The injected cells also contribute more to the mesenchyme, which may also be of interest.
## factor(tomato)TRUE
## Down 1
## NotSig 22
## Up 1## Coefficient: factor(tomato)TRUE
## logFC logCPM F PValue FDR
## ExE ectoderm -6.5663 13.02 66.267 1.352e-10 3.245e-09
## Mesenchyme 1.1652 16.29 11.291 1.535e-03 1.841e-02
## Allantois 0.8345 15.51 5.312 2.555e-02 1.621e-01
## Cardiomyocytes 0.8484 14.86 5.204 2.701e-02 1.621e-01
## Neural crest -0.7706 14.76 4.106 4.830e-02 2.149e-01
## Endothelium 0.7519 14.29 3.912 5.371e-02 2.149e-01
## Erythroid3 -0.6431 17.28 3.604 6.367e-02 2.183e-01
## Haematoendothelial progenitors 0.6581 14.72 3.124 8.351e-02 2.505e-01
## ExE mesoderm 0.3805 15.68 1.181 2.827e-01 6.258e-01
## Pharyngeal mesoderm 0.3793 15.72 1.169 2.850e-01 6.258e-016.3 Handling composition effects
6.3.1 Background
As mentioned above, we do not use calcNormFactors() in our default DA analysis.
This normalization step assumes that most of the input features are not different between conditions.
While this assumption is reasonable for most types of gene expression data, it is generally too strong for cell type abundance - most experiments consist of only a few cell types that may all change in abundance upon perturbation.
Thus, our default approach is to only normalize based on the total number of cells in each sample, which means that we are effectively testing for differential proportions between conditions.
Unfortunately, the use of the total number of cells leaves us susceptible to composition effects. For example, a large increase in abundance for one cell subpopulation will introduce decreases in proportion for all other subpopulations - which is technically correct, but may be misleading if one concludes that those other subpopulations are decreasing in abundance of their own volition. If composition biases are proving problematic for interpretation of DA results, we have several avenues for removing them or mitigating their impact by leveraging a priori biological knowledge.
6.3.2 Assuming most labels do not change
If it is possible to assume that most labels (i.e., cell types) do not change in abundance, we can use calcNormFactors() to compute normalization factors.
This seems to be a fairly reasonable assumption for the WT chimeras where the injection is expected to have only a modest effect at most.
## [1] 1.0055 1.0833 1.1658 0.7614 1.0616 0.9743We then proceed with the remainder of the edgeR analysis, shown below in condensed format. Many of the positive log-fold changes are shifted towards zero, consistent with the removal of composition biases from the presence of extra-embryonic ectoderm in only background cells. In particular, the mesenchyme is no longer significantly DA after injection.
y.ab2 <- estimateDisp(y.ab2, design, trend="none")
fit.ab2 <- glmQLFit(y.ab2, design, robust=TRUE, abundance.trend=FALSE)
res2 <- glmQLFTest(fit.ab2, coef=ncol(design))
topTags(res2, n=10)## Coefficient: factor(tomato)TRUE
## logFC logCPM F PValue FDR
## ExE ectoderm -6.9215 13.17 70.364 5.738e-11 1.377e-09
## Mesenchyme 0.9513 16.27 6.787 1.219e-02 1.143e-01
## Neural crest -1.0032 14.78 6.464 1.429e-02 1.143e-01
## Erythroid3 -0.8504 17.35 5.517 2.299e-02 1.380e-01
## Cardiomyocytes 0.6400 14.84 2.735 1.047e-01 4.809e-01
## Allantois 0.6054 15.51 2.503 1.202e-01 4.809e-01
## Forebrain/Midbrain/Hindbrain -0.4943 16.55 1.928 1.713e-01 5.178e-01
## Endothelium 0.5482 14.27 1.917 1.726e-01 5.178e-01
## Erythroid2 -0.4818 16.00 1.677 2.015e-01 5.373e-01
## Haematoendothelial progenitors 0.4262 14.73 1.185 2.818e-01 6.240e-016.3.3 Removing the offending labels
Another approach is to repeat the analysis after removing DA clusters containing many cells.
This provides a clearer picture of the changes in abundance among the remaining clusters.
Here, we remove the extra-embryonic ectoderm and reset the total number of cells for all samples with keep.lib.sizes=FALSE.
offenders <- "ExE ectoderm"
y.ab3 <- y.ab[setdiff(rownames(y.ab), offenders),, keep.lib.sizes=FALSE]
y.ab3$samples ## group lib.size norm.factors batch cell barcode sample stage
## 5 1 2268 1 5 cell_9769 AAACCTGAGACTGTAA 5 E8.5
## 6 1 993 1 6 cell_12180 AAACCTGCAGATGGCA 6 E8.5
## 7 1 2708 1 7 cell_13227 AAACCTGAGACAAGCC 7 E8.5
## 8 1 2749 1 8 cell_16234 AAACCTGCAAACCCAT 8 E8.5
## 9 1 4009 1 9 cell_19332 AAACCTGCAACGATCT 9 E8.5
## 10 1 6224 1 10 cell_23875 AAACCTGAGGCATGTG 10 E8.5
## tomato pool stage.mapped celltype.mapped closest.cell
## 5 TRUE 3 E8.25 Mesenchyme cell_24159
## 6 FALSE 3 E8.25 Somitic mesoderm cell_63247
## 7 TRUE 4 E8.5 Somitic mesoderm cell_25454
## 8 FALSE 4 E8.25 ExE mesoderm cell_139075
## 9 TRUE 5 E8.0 ExE mesoderm cell_116116
## 10 FALSE 5 E8.5 Forebrain/Midbrain/Hindbrain cell_39343
## doub.density sizeFactor label
## 5 0.029850 1.6349 19
## 6 0.291916 2.5981 6
## 7 0.601740 1.5939 17
## 8 0.004733 0.8707 9
## 9 0.079415 0.8933 15
## 10 0.040747 0.3947 1y.ab3 <- estimateDisp(y.ab3, design, trend="none")
fit.ab3 <- glmQLFit(y.ab3, design, robust=TRUE, abundance.trend=FALSE)
res3 <- glmQLFTest(fit.ab3, coef=ncol(design))
topTags(res3, n=10)## Coefficient: factor(tomato)TRUE
## logFC logCPM F PValue FDR
## Mesenchyme 1.1274 16.32 11.501 0.001438 0.03308
## Allantois 0.7950 15.54 5.231 0.026836 0.18284
## Cardiomyocytes 0.8104 14.90 5.152 0.027956 0.18284
## Neural crest -0.8085 14.80 4.903 0.031798 0.18284
## Erythroid3 -0.6808 17.32 4.387 0.041743 0.19202
## Endothelium 0.7151 14.32 3.830 0.056443 0.21636
## Haematoendothelial progenitors 0.6189 14.76 2.993 0.090338 0.29683
## Def. endoderm 0.4911 12.43 1.084 0.303347 0.67818
## ExE mesoderm 0.3419 15.71 1.036 0.314058 0.67818
## Pharyngeal mesoderm 0.3407 15.76 1.025 0.316623 0.67818A similar strategy can be used to focus on proportional changes within a single subpopulation of a very heterogeneous data set. For example, if we collected a whole blood data set, we could subset to T cells and test for changes in T cell subtypes (memory, killer, regulatory, etc.) using the total number of T cells in each sample as the library size. This avoids detecting changes in T cell subsets that are driven by compositional effects from changes in abundance of, say, B cells in the same sample.
6.3.4 Testing against a log-fold change threshold
Here, we assume that composition bias introduces a spurious log2-fold change of no more than \(\tau\) for a non-DA label. This can be roughly interpreted as the maximum log-fold change in the total number of cells caused by DA in other labels. (By comparison, fold-differences in the totals due to differences in capture efficiency or the size of the original cell population are not attributable to composition bias and should not be considered when choosing \(\tau\).) We then mitigate the effect of composition biases by testing each label for changes in abundance beyond \(\tau\) (McCarthy and Smyth 2009; Lun, Richard, and Marioni 2017).
## factor(tomato)TRUE
## Down 1
## NotSig 23
## Up 0## Coefficient: factor(tomato)TRUE
## logFC unshrunk.logFC logCPM PValue
## ExE ectoderm -6.5663 -7.0015 13.02 2.626e-09
## Mesenchyme 1.1652 1.1658 16.29 1.323e-01
## Cardiomyocytes 0.8484 0.8498 14.86 3.796e-01
## Allantois 0.8345 0.8354 15.51 3.975e-01
## Neural crest -0.7706 -0.7719 14.76 4.501e-01
## Endothelium 0.7519 0.7536 14.29 4.665e-01
## Haematoendothelial progenitors 0.6581 0.6591 14.72 5.622e-01
## Def. endoderm 0.5262 0.5311 12.40 5.934e-01
## Erythroid3 -0.6431 -0.6432 17.28 6.118e-01
## Caudal Mesoderm -0.3996 -0.4036 12.09 6.827e-01
## FDR
## ExE ectoderm 6.303e-08
## Mesenchyme 9.950e-01
## Cardiomyocytes 9.950e-01
## Allantois 9.950e-01
## Neural crest 9.950e-01
## Endothelium 9.950e-01
## Haematoendothelial progenitors 9.950e-01
## Def. endoderm 9.950e-01
## Erythroid3 9.950e-01
## Caudal Mesoderm 9.950e-01The choice of \(\tau\) can be loosely motivated by external experimental data. For example, if we observe a doubling of cell numbers in an in vitro system after treatment, we might be inclined to set \(\tau=1\). This ensures that any non-DA subpopulation is not reported as being depleted after treatment. Some caution is still required, though - even if the external numbers are accurate, we need to assume that cell capture efficiency is (on average) equal between conditions to justify their use as \(\tau\). And obviously, the use of a non-zero \(\tau\) will reduce power to detect real changes when the composition bias is not present.
Session Info
R version 4.1.0 (2021-05-18)
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit)
Running under: Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /home/biocbuild/bbs-3.13-bioc/R/lib/libRblas.so
LAPACK: /home/biocbuild/bbs-3.13-bioc/R/lib/libRlapack.so
locale:
[1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
[3] LC_TIME=en_US.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=C
[5] LC_MONETARY=en_US.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8
[7] LC_PAPER=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
[9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
[11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_US.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
attached base packages:
[1] parallel stats4 stats graphics grDevices utils datasets
[8] methods base
other attached packages:
[1] edgeR_3.34.0 limma_3.48.0
[3] SingleCellExperiment_1.14.0 SummarizedExperiment_1.22.0
[5] Biobase_2.52.0 GenomicRanges_1.44.0
[7] GenomeInfoDb_1.28.0 IRanges_2.26.0
[9] S4Vectors_0.30.0 BiocGenerics_0.38.0
[11] MatrixGenerics_1.4.0 matrixStats_0.58.0
[13] BiocStyle_2.20.0 rebook_1.2.0
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] statmod_1.4.36 locfit_1.5-9.4 xfun_0.23
[4] bslib_0.2.5.1 splines_4.1.0 lattice_0.20-44
[7] htmltools_0.5.1.1 yaml_2.2.1 XML_3.99-0.6
[10] rlang_0.4.11 jquerylib_0.1.4 CodeDepends_0.6.5
[13] GenomeInfoDbData_1.2.6 stringr_1.4.0 zlibbioc_1.38.0
[16] codetools_0.2-18 evaluate_0.14 knitr_1.33
[19] highr_0.9 Rcpp_1.0.6 filelock_1.0.2
[22] BiocManager_1.30.15 DelayedArray_0.18.0 graph_1.70.0
[25] jsonlite_1.7.2 XVector_0.32.0 dir.expiry_1.0.0
[28] digest_0.6.27 stringi_1.6.2 bookdown_0.22
[31] grid_4.1.0 tools_4.1.0 bitops_1.0-7
[34] magrittr_2.0.1 sass_0.4.0 RCurl_1.98-1.3
[37] Matrix_1.3-3 rmarkdown_2.8 R6_2.5.0
[40] compiler_4.1.0 References
Finak, G., J. Frelinger, W. Jiang, E. W. Newell, J. Ramey, M. M. Davis, S. A. Kalams, S. C. De Rosa, and R. Gottardo. 2014. “OpenCyto: an open source infrastructure for scalable, robust, reproducible, and automated, end-to-end flow cytometry data analysis.” PLoS Comput. Biol. 10 (8): e1003806.
Lun, A. T. L., A. C. Richard, and J. C. Marioni. 2017. “Testing for differential abundance in mass cytometry data.” Nat. Methods 14 (7): 707–9.
McCarthy, D. J., and G. K. Smyth. 2009. “Testing significance relative to a fold-change threshold is a TREAT.” Bioinformatics 25 (6): 765–71.
Pijuan-Sala, B., J. A. Griffiths, C. Guibentif, T. W. Hiscock, W. Jawaid, F. J. Calero-Nieto, C. Mulas, et al. 2019. “A Single-Cell Molecular Map of Mouse Gastrulation and Early Organogenesis.” Nature 566 (7745): 490–95.
6.4 Comments on interpretation
6.4.1 DE or DA? Two sides of the same coin
While useful, the distinction between DA and DE analyses is inherently artificial for scRNA-seq data. This is because the labels used in the former are defined based on the genes to be tested in the latter. To illustrate, consider a scRNA-seq experiment involving two biological conditions with several shared cell types. We focus on a cell type \(X\) that is present in both conditions but contains some DEGs between conditions. This leads to two possible outcomes:
We have described the example above in terms of clustering, but the same arguments apply for any labelling strategy based on the expression profiles, e.g., automated cell type assignment (Basic Chapter 7). Moreover, the choice between outcomes 1 and 2 is made implicitly by the combined effect of the data merging, clustering and label assignment procedures. For example, differences between conditions are more likely to manifest as DE for coarser clusters and as DA for finer clusters, but this is difficult to predict reliably.
The moral of the story is that DA and DE analyses are simply two different perspectives on the same phenomena. For any comprehensive characterization of differences between populations, it is usually necessary to consider both analyses. Indeed, they complement each other almost by definition, e.g., clustering parameters that reduce DE will increase DA and vice versa.
6.4.2 Sacrificing biology by integration
Earlier in this chapter, we defined clusters from corrected values after applying
fastMNN()to cells from all samples in the chimera dataset. Alert readers may realize that this would result in the removal of biological differences between our conditions. Any systematic difference in expression caused by injection would be treated as a batch effect and lost when cells from different samples are aligned to the same coordinate space. Now, one may not consider injection to be an interesting biological effect, but the same reasoning applies for other conditions, e.g., integration of wild-type and knock-out samples (Section 5) would result in the loss of any knock-out effect in the corrected values.This loss is both expected and desirable. As we mentioned in Section 3, the main motivation for performing batch correction is to enable us to characterize population heterogeneity in a consistent manner across samples. This remains true in situations with multiple conditions where we would like one set of clusters and annotations that can be used as common labels for the DE or DA analyses described above. The alternative would be to cluster each condition separately and to attempt to identify matching clusters across conditions - not straightforward for poorly separated clusters in contexts like differentiation.
It may seem distressing to some that a (potentially very interesting) biological difference between conditions is lost during correction. However, this concern is largely misplaced as the correction is only ever used for defining common clusters and annotations. The DE analysis itself is performed on pseudo-bulk samples created from the uncorrected counts, preserving the biological difference and ensuring that it manifests in the list of DE genes for affected cell types. Of course, if the DE is strong enough, it may result in a new condition-specific cluster that would be captured by a DA analysis as discussed in Section 6.4.1.
One final consideration is the interaction of condition-specific expression with the assumptions of each batch correction method. For example, MNN correction assumes that the differences between samples are orthogonal to the variation within samples. Arguably, this assumption is becomes more questionable if the between-sample differences are biological in nature, e.g., a treatment effect that makes one cell type seem more transcriptionally similar to another may cause the wrong clusters to be aligned across conditions. As usual, users will benefit from the diagnostics described in Chapter 1 and a healthy dose of skepticism.