---
title: "GenomicSuperSignature - Quickstart"
author: "Sehyun Oh"
date: "`r format(Sys.time(), '%B %d, %Y')`"
abstract: |
This vigenette demostrates a basic usage of GenomicSuperSignature. More
extensive and biology-relavant use cases are available [**HERE**](https://shbrief.github.io/GenomicSuperSignaturePaper/).
vignette: >
%\VignetteEngine{knitr::rmarkdown}
%\VignetteIndexEntry{Quickstart}
%\VignetteEncoding{UTF-8}
output:
BiocStyle::html_document:
number_sections: yes
toc: yes
toc_depth: 4
---
```{r setup, include = FALSE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
comment = "#>", collapse = TRUE, message = FALSE, warning = FALSE,
fig.align='center'
)
```
# Setup
## Install and load package
```{r eval = FALSE}
if (!require("BiocManager"))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("GenomicSuperSignature")
BiocManager::install("bcellViper")
```
```{r results="hide", message=FALSE, warning=FALSE}
library(GenomicSuperSignature)
library(bcellViper)
```
## Download RAVmodel
You can download GenomicSuperSignature from Google Cloud bucket using
`GenomicSuperSignature::getModel` function. Currently available models are
built from top 20 PCs of 536 studies (containing 44,890 samples) containing
13,934 common genes from each of 536 study's top 90% varying genes based on
their study-level standard deviation. There are two versions of this RAVmodel
annotated with different gene sets for GSEA - MSigDB C2 (`C2`) and three
priors from PLIER package (`PLIERpriors`).
The demo in this vignette is based on human B-cell expression data, so we are
using the `PLIERpriors` model annotated with blood-associated gene sets.
Note that the first interactive run of this code, you will be asked to allow
R to create a cache directory. The model file will be stored there and
subsequent calls to `getModel` will read from the cache.
```{r load_model}
RAVmodel <- getModel("PLIERpriors", load=TRUE)
RAVmodel
version(RAVmodel)
```
## Example dataset
The human B-cell dataset (Gene Expression Omnibus series GSE2350) consists of
211 normal and tumor human B-cell phenotypes. This dataset was generated on
Affymatrix HG-U95Av2 arrays and stored in an ExpressionSet object with 6,249
features x 211 samples.
```{r message=FALSE, warning=FALSE}
data(bcellViper)
dset
```
You can provide your own expression dataset in any of these formats: simple
matrix, ExpressionSet, or SummarizedExperiment. Just make sure that genes are
in a 'symbol' format.
# Which RAV best represents the dataset?
`validate` function calculates validation score, which provides a quantitative
representation of the relevance between a new dataset and RAV. RAVs that give
the validation score is called _*validated RAV*_. The validation results can
be displayed in different ways for more intuitive interpretation.
```{r}
val_all <- validate(dset, RAVmodel)
head(val_all)
```
## HeatmapTable
`heatmapTable` takes validation results as its input and displays them into
a two panel table: the top panel shows the average silhouette width (avg.sw)
and the bottom panel displays the validation score.
`heatmapTable` can display different subsets of the validation output. For
example, if you specify `scoreCutoff`, any validation result above that score
will be shown. If you specify the number (n) of top validation results through
`num.out`, the output will be a n-columned heatmap table. You can also use the
average silhouette width (`swCutoff`), the size of cluster (`clsizecutoff`),
one of the top 8 PCs from the dataset (`whichPC`).
Here, we print out top 5 validated RAVs with average silhouette width above 0.
```{r out.height="80%", out.width="80%", message=FALSE, warning=FALSE}
heatmapTable(val_all, RAVmodel, num.out = 5, swCutoff = 0)
```
## Interactive Graph
Under the default condition, `plotValidate` plots validation results of all non
single-element RAVs in one graph, where x-axis represents average silhouette
width of the RAVs (a quality control measure of RAVs) and y-axis represents
validation score. We recommend users to focus on RAVs with higher validation
score and use average silhouette width as a secondary criteria.
```{r out.height="75%", out.width="75%", plotValidate_function}
plotValidate(val_all, interactive = FALSE)
```
Note that `interactive = TRUE` will result in a zoomable, interactive plot
that included tooltips.
You can hover each data point for more information:
- **sw** : the average silhouette width of the cluster
- **score** : the top validation score between 8 PCs of the dataset and RAVs
- **cl_size** : the size of RAVs, represented by the dot size
- **cl_num** : the RAV number. You need this index to find more information
about the RAV.
- **PC** : test dataset's PC number that validates the given RAV. Because we
used top 8 PCs of the test dataset for validation, there are 8 categories.
If you double-click the PC legend on the right, you will enter an
individual display mode where you can add an additional group of data
point by single-click.
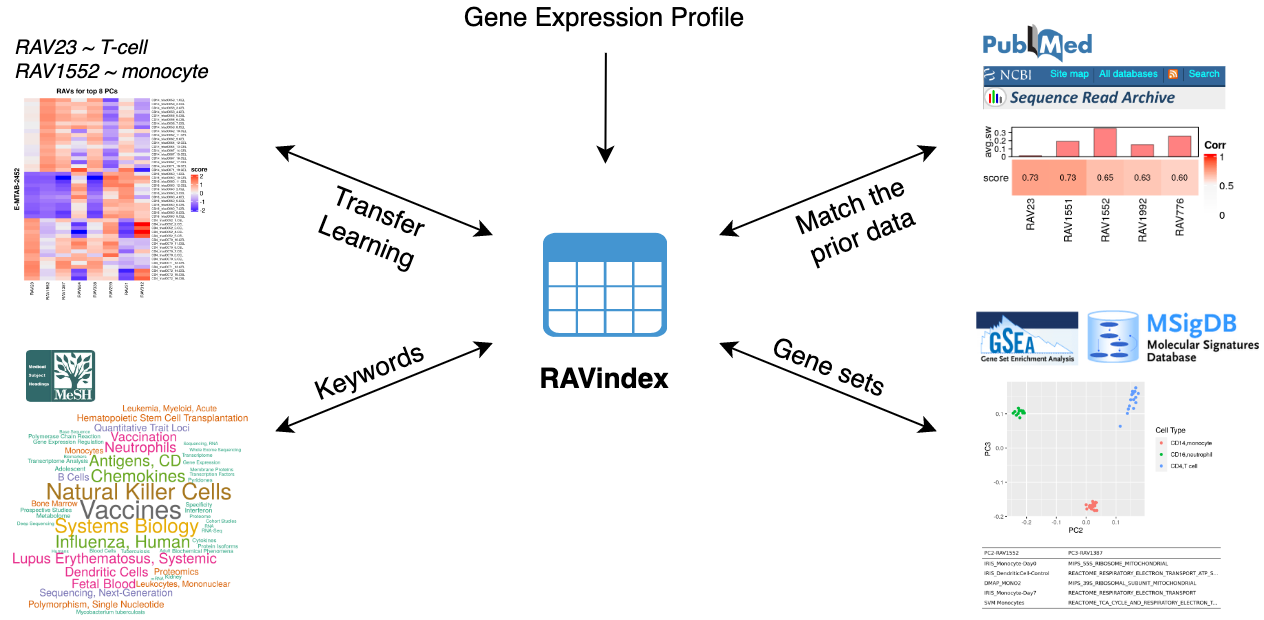
# What kinds of information can you access through RAV?
GenomicSuperSignature connects different public databases and prior information
through RAVmodel, creating the knowledge graph illustrated below. Through RAVs,
you can access and explore the knowledge graph from multiple entry points such
as gene expression profiles, publications, study metadata, keywords in MeSH
terms and gene sets.
 ## MeSH terms in wordcloud
You can draw a wordcloud with the enriched MeSH terms of RAVs. Based on the
heatmap table above, three RAVs (2538, 1139, and 884) show the high validation
scores with the positive average silhouette widths, so we draw wordclouds of
those RAVs using `drawWordcloud` function. You need to provide RAVmodel and
the index of the RAV you are interested in.
Index of validated RAVs can be easily collected using `validatedSingatures`
function, which outputs the validated index based on `num.out`, PC from dataset
(`whichPC`) or any `*Cutoff` arguments in the same way as `heatmapTable`. Here,
we choose the top 3 RAVs with the average silhouette width above 0, which will
returns RAV2538, RAV1139, and RAV884 as we discussed above.
```{r}
validated_ind <- validatedSignatures(val_all, RAVmodel, num.out = 3,
swCutoff = 0, indexOnly = TRUE)
validated_ind
```
And we plot the wordcloud of those three RAVs.
```{r out.height="60%", out.width="60%"}
set.seed(1) # only if you want to reproduce identical display of the same words
drawWordcloud(RAVmodel, validated_ind[1])
drawWordcloud(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2])
drawWordcloud(RAVmodel, validated_ind[3])
```
## GSEA
### Associated gene sets of validated RAV
You can directly access the GSEA outputs for each RAV using `annotateRAV`
function. Based on the wordclouds, RAV1139 seems to be associated with B-cell.
```{r}
annotateRAV(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2]) # RAV1139
```
If you want to check the enriched pathways for multiple RAVs, use
`subsetEnrichedPathways` function instead.
```{r}
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2], include_nes = TRUE)
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, validated_ind, include_nes = TRUE)
```
### Search enriched pathways through keyword
You can also find the RAVs annotated with the keyword-containing pathways using
`findSignature` function. Without the `k` argument, this function outputs a
data frame with two columns: the number of RAVs (`Freq` column) with the
different numbers of keyword-containing, enriched pathways
(`# of keyword-containing pathways` column).
Here, we used the keyword, "Bcell".
```{r}
findSignature(RAVmodel, "Bcell")
```
There are two RAVs with five keyword-containing pathways (row 6). We can check
which RAVs they are.
```{r}
findSignature(RAVmodel, "Bcell", k = 5)
```
Enriched pathways are ordered by NES and you can check the rank of any keyword-
containing pathways using `findKeywordInRAV`.
```{r}
findKeywordInRAV(RAVmodel, "Bcell", ind = 695)
```
You can check all enriched pathways of RAV using `subsetEnrichedPathways`
function. If `both=TRUE`, both the top and bottom enriched pathways will
be printed.
```{r}
## Chosen based on validation/MeSH terms
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, ind = validated_ind[2], n = 3, both = TRUE)
## Chosen based on enriched pathways
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, ind = 695, n = 3, both = TRUE)
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, ind = 953, n = 3, both = TRUE)
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, ind = 1994, n = 3, both = TRUE)
```
## Related prior studies
You can find the prior studies related to a given RAV using
`findStudiesInCluster` function.
```{r}
findStudiesInCluster(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2])
```
You can easily extract the study name with the `studyTitle=TRUE` parameter.
```{r}
findStudiesInCluster(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2], studyTitle = TRUE)
```
# Session Info
## MeSH terms in wordcloud
You can draw a wordcloud with the enriched MeSH terms of RAVs. Based on the
heatmap table above, three RAVs (2538, 1139, and 884) show the high validation
scores with the positive average silhouette widths, so we draw wordclouds of
those RAVs using `drawWordcloud` function. You need to provide RAVmodel and
the index of the RAV you are interested in.
Index of validated RAVs can be easily collected using `validatedSingatures`
function, which outputs the validated index based on `num.out`, PC from dataset
(`whichPC`) or any `*Cutoff` arguments in the same way as `heatmapTable`. Here,
we choose the top 3 RAVs with the average silhouette width above 0, which will
returns RAV2538, RAV1139, and RAV884 as we discussed above.
```{r}
validated_ind <- validatedSignatures(val_all, RAVmodel, num.out = 3,
swCutoff = 0, indexOnly = TRUE)
validated_ind
```
And we plot the wordcloud of those three RAVs.
```{r out.height="60%", out.width="60%"}
set.seed(1) # only if you want to reproduce identical display of the same words
drawWordcloud(RAVmodel, validated_ind[1])
drawWordcloud(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2])
drawWordcloud(RAVmodel, validated_ind[3])
```
## GSEA
### Associated gene sets of validated RAV
You can directly access the GSEA outputs for each RAV using `annotateRAV`
function. Based on the wordclouds, RAV1139 seems to be associated with B-cell.
```{r}
annotateRAV(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2]) # RAV1139
```
If you want to check the enriched pathways for multiple RAVs, use
`subsetEnrichedPathways` function instead.
```{r}
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2], include_nes = TRUE)
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, validated_ind, include_nes = TRUE)
```
### Search enriched pathways through keyword
You can also find the RAVs annotated with the keyword-containing pathways using
`findSignature` function. Without the `k` argument, this function outputs a
data frame with two columns: the number of RAVs (`Freq` column) with the
different numbers of keyword-containing, enriched pathways
(`# of keyword-containing pathways` column).
Here, we used the keyword, "Bcell".
```{r}
findSignature(RAVmodel, "Bcell")
```
There are two RAVs with five keyword-containing pathways (row 6). We can check
which RAVs they are.
```{r}
findSignature(RAVmodel, "Bcell", k = 5)
```
Enriched pathways are ordered by NES and you can check the rank of any keyword-
containing pathways using `findKeywordInRAV`.
```{r}
findKeywordInRAV(RAVmodel, "Bcell", ind = 695)
```
You can check all enriched pathways of RAV using `subsetEnrichedPathways`
function. If `both=TRUE`, both the top and bottom enriched pathways will
be printed.
```{r}
## Chosen based on validation/MeSH terms
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, ind = validated_ind[2], n = 3, both = TRUE)
## Chosen based on enriched pathways
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, ind = 695, n = 3, both = TRUE)
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, ind = 953, n = 3, both = TRUE)
subsetEnrichedPathways(RAVmodel, ind = 1994, n = 3, both = TRUE)
```
## Related prior studies
You can find the prior studies related to a given RAV using
`findStudiesInCluster` function.
```{r}
findStudiesInCluster(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2])
```
You can easily extract the study name with the `studyTitle=TRUE` parameter.
```{r}
findStudiesInCluster(RAVmodel, validated_ind[2], studyTitle = TRUE)
```
# Session Info
```{r}
sessionInfo()
```

